Kyanite
Kyanite 
General Category Minerals Chemical formula Al2SiO5
(aluminium silicate) Identification Color Blue; also green, white, grey, black Crystal habit Columnar; fibrous; bladed Crystal system Triclinic Cleavage [100] Perfect, [010] Imperfect Fracture Brittle Mohs Scalehardness 4.5-5 parallel to one axis
6.5-7 perpendicular to that axis Luster Vitreous; Pearly Streak White Diaphaneity Transparent to translucent Specific gravity 3.56 - 3.67 Refractive index 1.71 - 1.75 Pleochroism Trichroic, colorless to pale blue to blue Solubility None
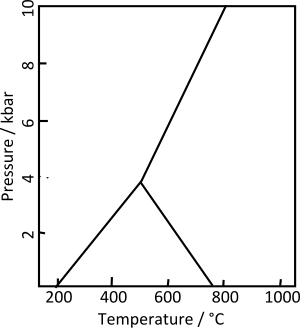
Phase diagram of the Aluminosilicates.[1] Kyanite from Brazil
Kyanite from BrazilKyanite, whose name derives from the Greek word kyanos, meaning blue, is a typically blue silicate mineral, commonly found in aluminium-rich metamorphic pegmatites and/orsedimentary rock. Kyanite inmetamorphic rocks generally indicates pressures higher than 4 kilobars. Although potentially stable at lower pressure and low temperature, the activity of water is usually high enough under such conditions that it is replaced by hydrous aluminosilicates such as muscovite, pyrophyllite, or kaolinite.
Kyanite is a member of the aluminosilicate series, which also includes the polymorphandalusite and the polymorph sillimanite. Kyanite is strongly anisotropic, in that its hardnessvaries depending on its crystallographic direction. While this is a feature of almost all minerals, in kyanite this anisotropism can be considered an identifying characteristic.
At temperatures above 1100 °C, kyanite decomposes into mullite and vitreous silica via the following reaction: 3(Al2O3·SiO2) → 3Al2O3·2SiO2 + SiO2. This transformation results in an expansion.[2]
Uses of kyanite
Kyanite is used primarily in refractory and ceramic products, including porcelain plumbing fixtures and dishware. It is also used in electrical insulators and abrasives. Kyanite has been used as a gemstone, though this use is limited by its anisotropism and perfect cleavage. Kyanite is one of the index minerals that are used to estimate the temperature, depth, and pressure at which a rock undergoes metamorphism. Finally, as with most minerals, kyanite is a collector's mineral.
Associated minerals
Kyanite is usually found in association with its polymorphs, as well as other silicate minerals. These include:
- andalusite, Al2SiO5
- sillimanite, Al2SiO5
- quartz, SiO2
- staurolite, Fe2Al9Si4O22(OH)2
- micas, AB2-3(X, Si)4O10(O,F,OH)2
- garnets, A3B2(SiO4)3
Alternative names
Kyanite has several alternative names, including disthene, munkrudite and cyanite. White-grey kyanite is also called rhaeticite.
Notes for identification
Kyanite's elongated, columnar crystals are usually a good first indication of the mineral, as well as its color (when the specimen is blue). Associated minerals are useful as well, especially the presence of the polymorphs or staurolite, which occur frequently with kyanite. However, the most useful characteristic in identifying kyanite is its anisotropism. If one suspects a specimen to be kyanite, verifying that it has two distinctly different hardnesses on perpendicular axes is a key to identification.

(aluminium silicate)
6.5-7 perpendicular to that axis


No comments:
Post a Comment